Browser Compatibility
WebGazer.js uses:
- getUserMedia/Stream API to get access to the webcam, which supports these browsers.
- IndexedDB (used by localforage) for storing data to the browser, which supports these browsers.
WebGazer.js is an eye tracking library that uses common webcams to infer the eye-gaze locations of web visitors on a page in real time. The eye tracking model it contains self-calibrates by watching web visitors interact with the web page and trains a mapping between the features of the eye and positions on the screen. WebGazer.js is written entirely in JavaScript and with only a few lines of code can be integrated in any website that wishes to better understand their visitors and transform their user experience. WebGazer.js runs entirely in the client browser, so no video data needs to be sent to a server, and it requires the user's consent to access their webcam.
Real time gaze prediction on most common browsers
No special hardware; WebGazer.js uses your webcam
Self-calibration from clicks and cursor movements
Easy to integrate with a few lines of JavaScript
Swappable components for eye detection
Multiple gaze prediction models
Open source since 2016 (over 10 years)
/* WebGazer.js library */
<script src="webgazer.js" type="text/javascript" >Be aware that when you do local development and you might need to run locally a simple http server that supports the https protocol.
Once the script is included, the webgazer object is introduced into the global namespace. webgazer has methods for controlling the operation of WebGazer.js allowing us to start and stop it, add callbacks, or change out modules. The two most important methods on webgazer are webgazer.begin() and webgazer.setGazeListener(). webgazer.begin() starts the data collection that enables the predictions, so it's important to call this early on. Once webgazer.begin() has been called, WebGazer.js is ready to start giving predictions. webgazer.setGazeListener() is a convenient way to access these predictions. This method invokes a callback you provide every few milliseconds to provide the current gaze location of a user. If you don't need constant access to this data stream, you may alternatively call webgazer.getCurrentPrediction() which will give you a prediction at the moment when it is called.
webgazer.setGazeListener(function(data, elapsedTime) {
if (data == null) {
return;
}
var xprediction = data.x; //these x coordinates are relative to the viewport
var yprediction = data.y; //these y coordinates are relative to the viewport
console.log(elapsedTime); //elapsed time is based on time since begin was called
}).begin();
Here is the alternate method of getting predictions where you can request a gaze prediction as needed.
var prediction = webgazer.getCurrentPrediction();
if (prediction) {
var x = prediction.x;
var y = prediction.y;
}
There are several features that WebGazer.js enables beyond the example shown so far.
WebGazer.js can save and restore the training data between browser sessions by storing data to the browser using localforage, which uses IndexedDB. This occurs automatically with every click in the window. If you want each user session to be independent make sure that you set window.saveDataAcrossSessions in main.js to false.
At the heart of WebGazer.js are the tracker and regression modules. The tracker module controls how eyes are detected and the regression module determines how the regression model is learned and how predictions are made based on the eye patches extracted from the tracker module. These modules can be swapped in and out at any time. We hope that this will make it easy to extend and adapt WebGazer.js and welcome any developers that want to contribute.
WebGazer.js requires the bounding box that includes the pixels from the webcam video feed that correspond to the detected eyes of the user. Currently we include one external library to detect the face and eyes.
webgazer.setTracker("TFFacemesh"); //set a tracker modulewebgazer.addTrackerModule("newTracker", NewTrackerConstructor); //add a new tracker moduleCurrently, MediaPipe Facemesh comes by default with WebGazer.js.
webgazer.setRegression("ridge"); //set a regression modulewebgazer.addRegressionModule("newReg", NewRegConstructor); //add a new regression moduleHere are all the regression modules that come by default with WebGazer.js. Community contributions introducing new modules are welcome on GitHub — keep in mind that they should be able to produce predictions very fast.
It may be necessary to pause the data collection and predictions of WebGazer.js for performance reasons.
webgazer.pause(); //WebGazer.js is now paused, no data will be collected and the gaze callback will not be executed
webgazer.resume(); //data collection resumes, gaze callback will be called again
We provide some useful functions and objects in webgazer.util. The webgazer.params object also contains some useful parameters to tweak to control video fidelity (trades off speed and accuracy) and sample rate for mouse movements.
webgazer.util.bound(prediction);
prediction.x; //now always in the bounds of the viewport
prediction.y; //now always in the bounds of the viewport
WebGazer.js uses:
The GitHub repository contains the source code and version history.
# Ensure NodeJS is downloaded: https://nodejs.org/en/download/
git clone https://github.com/brownhci/WebGazer.git
cd WebGazer
#install the dependencies
npm install
#build the project
npm run build
See how easy it is to integrate WebGazer.js on any webpage. With just a few clicks you will get real-time predictions. Follow the popup instructions to click through 9 calibration points on the screen whilst looking at the cursor.
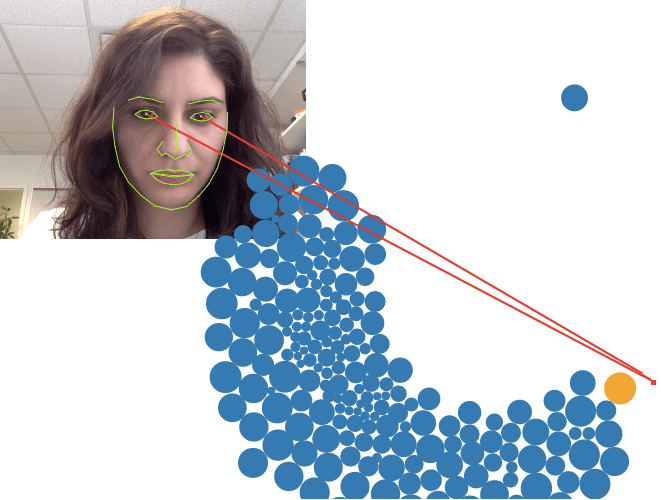
Move the orange ball with your eyes and create collisions with the blue balls. Train WebGazer.js by clicking in various locations within the screen, while looking at your cursor.
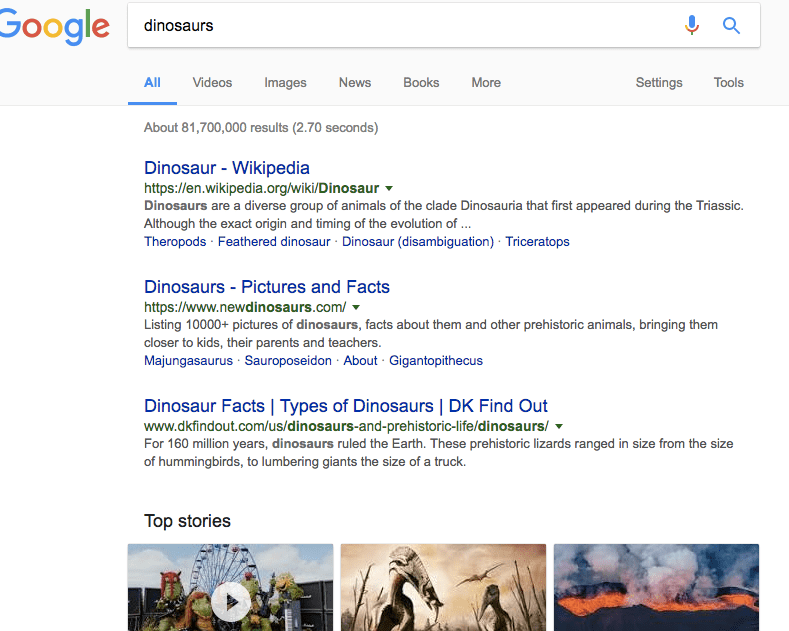
We have created SearchGazer.js, a library that incorporates WebGazer in Search Engines such as Bing and Google. Note that this uses an older version of WebGazer, so is here just as a legacy demo.
Note: The current iteration of WebGazer no longer corresponds with the WebGazer described in the following publications. The legacy version as described in the paper can be found in the commit history on GitHub.
If you use WebGazer.js please cite:
@inproceedings{papoutsaki2016webgazer,
author = {Alexandra Papoutsaki and Patsorn Sangkloy and James Laskey and Nediyana Daskalova and Jeff Huang and James Hays},
title = {WebGazer: Scalable Webcam Eye Tracking Using User Interactions},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI)},
pages = {3839--3845},
year = {2016},
organization={AAAI}
}
If you use SearchGazer.js please cite the following paper:
@inproceedings{papoutsaki2017searchgazer,
author = {Alexandra Papoutsaki and James Laskey and Jeff Huang},
title = {SearchGazer: Webcam Eye Tracking for Remote Studies of Web Search},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the ACM SIGIR Conference on Human Information Interaction \& Retrieval (CHIIR)},
year = {2017},
organization={ACM}
}
For the WebGazer webcam dataset and findings about gaze behavior during typing:
@inproceedings{papoutsaki2018eye,
title={The eye of the typer: a benchmark and analysis of gaze behavior during typing},
author={Papoutsaki, Alexandra and Gokaslan, Aaron and Tompkin, James and He, Yuze and Huang, Jeff},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 2018 ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research \& Applications},
pages={16},
year={2018},
organization={ACM}
}
Websites that have featured WebGazer.js:
Online discussions and shares in:
Want to help? See these open issues tagged "help wanted"
Webgazer is based on the research originally done at Brown University, with recent work and maintenance jointly between Pomona College and Brown University. The current maintainer is Jeff Huang.
The calibration example file was developed in the context of a course project with the aim to improve the feedback of WebGazer, proposed by Dr. Gerald Weber and his team Dr. Clemens Zeidler and Kai-Cheung Leung.
This research is supported by NSF grants IIS-1464061, IIS-1552663, a Seed Award from the Center for Vision Research at Brown University, and the Brown University Salomon Award.
Copyright (C) 2016-2026 Brown WebGazer Team
Licensed under GPLv3